Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 by monolayer hexagonal boron nitride coating for improved photo- and thermionic-cathodes
by monolayer hexagonal boron nitride coating for improved photo- and thermionic-cathodesYamaguchi, Hisato*; Yusa, Ryunosuke*; Wang, G.*; Pettes, M. T.*; Liu, F.*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Abukawa, Tadashi*; Moody, N. A.*; Ogawa, Shuichi*
Applied Physics Letters, 122(14), p.141901_1 - 141901_7, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:81.68(Physics, Applied)A lowering of work function for LaB by monolayer hexagonal BN coating is reported. Photoemission electron microcopy (PEEM) and thermionic emission electron microscopy (TEEM) both revealed that the hBN coated region of a LaB
by monolayer hexagonal BN coating is reported. Photoemission electron microcopy (PEEM) and thermionic emission electron microscopy (TEEM) both revealed that the hBN coated region of a LaB (100) single crystal has lower work function compared to the bare (i.e., non-coated) and graphene coated regions. A larger decrease of work function for the hBN coated LaB
(100) single crystal has lower work function compared to the bare (i.e., non-coated) and graphene coated regions. A larger decrease of work function for the hBN coated LaB (100) compared to graphene coated LaB
(100) compared to graphene coated LaB (100) was qualitatively supported by our density functional theory (DFT) calculations. Adding an oxide layer in the calculations improved consistency between the calculation and experimental results. We followed up our calculations with synchrotron-radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (SR-XPS) and confirmed the presence of an oxide layer on our LaB
(100) was qualitatively supported by our density functional theory (DFT) calculations. Adding an oxide layer in the calculations improved consistency between the calculation and experimental results. We followed up our calculations with synchrotron-radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (SR-XPS) and confirmed the presence of an oxide layer on our LaB .
.
Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Hoshako Riyo No Tebiki, p.130 - 138, 2019/02
The educational book on next-generation synchrotron radiation usage is partially written. This book is being planned by several professors at Tohoku University. In this book, the contents which have already reported in our recent paper [Appl. Phys. Lett. 112 (2018) 021603.] are mainly written. The future perspective on photoemission electron microscopy using next generation synchrotron radiation and its possibility to analyze environmental samples and insulating functional materials are also described.
Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Kobayashi, Toru; Shimoyama, Iwao; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Nishihata, Yasuo; Kogure, Toshihiro*; Okochi, Takuo*; Yasui, Akira*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 112(2), p.021603_1 - 021603_5, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:29.69(Physics, Applied)A synchrotron radiation photoemission electron microscope (SR-PEEM) was applied to demonstrate pinpoint analysis of micrometer-sized weathered biotite clay particles with artificially adsorbed cesium (Cs) atoms. Despite the insulating properties of the clay, we observed the spatial distributions of constituent elements (Si, Al, Cs, Mg, Fe) without charging issues. We found that Cs atoms were likely to be adsorbed evenly over the entire particle. Spatially-resolved X-ray absorption spectra (XAS) of the Cs M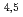 -edge region showed Cs to be present in a monocation state (Cs
-edge region showed Cs to be present in a monocation state (Cs ). Further pinpoint XAS measurements were also performed at the Fe L
). Further pinpoint XAS measurements were also performed at the Fe L -edge to determine the chemical valence of the Fe atoms. Our results demonstrate the utility of SR-PEEM as a tool for spatially-resolved chemical analyses of various environmental substances, which is not limited by the poor conductivity of samples.
-edge to determine the chemical valence of the Fe atoms. Our results demonstrate the utility of SR-PEEM as a tool for spatially-resolved chemical analyses of various environmental substances, which is not limited by the poor conductivity of samples.
Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji; Hirao, Norie; Honda, Mitsunori; Izumi, Toshinori; Ikeura, Hiromi*
Molecular Crystals and Liquid Crystals, 622(1), p.44 - 49, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The molecular orientation is one of the important factors for controlling various properties in organic semiconductor materials. Films are usually heterogeneous. Thus they exist as a mixture of microscopic domains which have a variety of orientation directions. Therefore, it is essential to observe selectively microscopic domains with different orientation direction. In this work, we have developed the photoelectron emission microscopy (PEEM) system combined with the linearly polarized vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) light or synchrotron radiation (SR) X-rays. PEEM images (FOV = ca.50 micro m) for poly(3-hexylthiophene), P3HT thin films were observed under the UV irradiation with various polarization angles, including in-plain and out-of-plain polarization. Morphologies at some bright parts are different each other. The resultant observation suggests that it enables us to distinguish oriented micro-domains with specific directions of polymer chain axis from other amorphous parts.
Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Honda, Mitsunori; Izumi, Toshinori; Ikeura, Hiromi*
Photon Factory Activity Report 2013, Part B, P. 546, 2014/00
The molecular orientation is one of the important factors for controlling various properties in organic semiconductor materials. Films are usually heterogeneous. Thus they exist as a mixture of microscopic domains which have a variety of orientation directions. Therefore, it is essential to observe selectively microscopic domains with different orientation direction. In this work, we have developed the photoelectron emission microscope (PEEM) system combined with the linearly polarized vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) light or synchrotron radiation (SR) X-rays. PEEM images for poly(3-hexylthiophene), P3HT thin films were observed under synchrotron X-ray irradiation with linearly polarization. In conclusion, it was found that PEEM with polarized synchrotron can be a powerful tool that gives information of molecular orientation in nano-meter scale.
Terauchi, Masami*; Koike, Masato
Microscopy and Microanalysis, 9(S02), p.894 - 895, 2003/08
We have been developing a high energy-resolution soft-X-ray spectrometer for a transmission electron microscope to obtain the information of the density of states (DOS) of the valence band (occupied states) from identified small specimen areas. We have designed and produced a new grating. The new varied-line-spacing laminar-type holographic grating was designed to have a focal distance of about 50 cm. An energy resolution of about 0.7 eV is expected for X-ray energy of about 1000 eV.
Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Kobayashi, Toru; Shimoyama, Iwao; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Nishihata, Yasuo; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Kogure, Toshihiro*; Motai, Satoko*; et al.
no journal, ,
Fundamental researches on adsorption state of radiaoactive Cs in clay mineral (aluminosilicate) have become important from the virewpoints of development of decontamination or volume-reduction techniques since the accident of Fukushima Daiiichi Nuclear Power Station. Pinpoint surface chemical analysis with nanometer spatial resolutions focusing on a target sample has been needed. In this presentation, I will show our recent work on nanoscale pinpoint surface chemical analysis for Cs-containing clay mineral by means of synchrotron radiation PEEM at BL17SU in SPring-8.
Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Kobayashi, Toru; Shimoyama, Iwao; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Nishihata, Yasuo; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Kogure, Toshihiro*; Motai, Satoko*; et al.
no journal, ,
Pinpoint chemical analysis for Cs-adsorbed vermiculite was performed by using synchrotron radiation photoelectron emission microscopy (SR-PEEM). It was found that Cs is distributed through the micro-size clay particles and we also succeeded to measure pinpoint X-ray absorption spectra for constituent element simultaneously. Furthermore, we precisely confirmed the existence of Fe in the sample.
Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Honda, Mitsunori; Hirao, Norie; Ikeura, Hiromi*
no journal, ,
High degrees of molecular orientation play a crucial role in the improvement of electronic properties in organic semiconductors. Thus, it is essential to selectively characterize materials with different orientation direction in microscopic domains. So far, we have strived to observe orientation of organic-semiconductors in microscopic domains using the photoelectron emission microscopy (PEEM) system with excitation by linearly polarized ultraviolet (UV) light from mercury lamp and synchrotron X-rays.
Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
In this symposium, we present recent synchrotron radiation photoelectron emission microscopy (SR-PEEM) study on Cs mapping and its electronic states in clay mineral which is artificially adsorbed in. The experiments was conducted using permanent PEEM apparatus at BL17SU in SPring-8. In addition, the future expectation of synchrotron based microscopy for surface science research, especially surface chemistry will be discussed.
Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
Decontamination of Cs trapped in clays is considered to be difficult because Cs atoms tightly bind to the clays. Therefore, the development of the methods to efficiently remove Cs from polluted areas has become a matter of great importance and has motivated research into basic understanding Cs adsorption to clay and its physicochemical properties. In this study, a synchrotron radiation photoemission electron microscope (SR-PEEM) was applied to demonstrate pinpoint analysis of micrometer-sized weathered biotite clay particles with artificially adsorbed non-radioactive Cs. Despite the insulating properties of the clay, we observed the spatial distributions of constituent elements with nanometer resolution without charging issues through a proper surface treatment. Pinpoint XAS spectra indicated the chemical states of Fe and Cs. The results strongly suggest that Cs adsorption took place via electrical charge compensation mechanisms. Further technical developments are required to apply to real-world samples with extremely low Cs content; however, we succeeded the first step towards applying this method to nanoscale analysis of Cs-adsorbed clay minerals.
Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
In this conference on surface science, the results of pinpoint analysis of clay minerals artificially containing Cs using synchrotron radiation photoemission electron microscopy are talked as an invited lecture. Nano-scaled realspace analysis of distribution maps of the constituent elements and chemical states of both Cs and Fe atoms are described to discuss the model of Cs adsorption into clay minerals. Future perspective of the application of synchrotron radiation photoemission electron microscopy to various kinds of research fields are also talked.
Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
In this symposium, the results of nanoscale spatial analysis of clay minerals artificially containing Cs using synchrotron radiation photoemission electron microscopy are talked as an invited tutorial. Despite of its insulating properties, precise analysis of distribution maps of the constituent elements and chemical states of both Cs and Fe atoms were succeeded due to the proper sample treatments. The model of Cs adsorption into clay minerals is discussed based on the data of pinpoint X-ray absorption spectra for Cs and Fe core-levels. Future perspective of the application of synchrotron radiation photoemission electron microscopy are also talked.
Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
After the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in 2011, decontamination of radioactive cesium is a major concern for recovering from the environmental damage. It is generally known that Cs is irreversibly incorporated into clay minerals such as weathered biotite. Therefore, the development of efficient way to remove Cs has motivated research into understanding Cs adsorption and its physicochemical properties. Synchrotron radiation photoemission electron microscope (SR-PEEM) was applied to perform the pinpoint analysis of micrometer-sized weathered biotite particles with artificially adsorbed Cs. Spatial distributions of constituent elements were observed with nanometer resolution. Spatially resolved X-ray absorption spectra of the Cs M- and Fe L-edges were measured to determine the chemical states of each atom. The results demonstrate the utility of SR-PEEM as a tool for nanoscale chemical analyses of various environmental substances.
Yoshigoe, Akitaka
no journal, ,
A synchrotron radiation photoemission electron microscope (SR-PEEM) probing photoelectrons emitted from samples is an useful microscope with surface sensitive and nanoscale spatial resolution. The electron lens-system facilitates the enlargement and reduction of the sample image, and enables pinpoint chemical analysis by high energy resolution X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS). It has many advantages over scanning and transmission microscopes because it can observe samples without any preparations such as reduction of the sample thickness. In this talk, an application of SR-PEEM for elucidation of the adsorption states of radioactive Cs in clay minerals due to 1F accident will be shown. To overcome insulating properties of clay, an thin film was deposited on the sample surface. After this treatment. clear Cs map and pinpoint XAS spectra for Cs M-edge XAS for weathered biotite clay minerals with Cs were obtained to giving important findings on Cs adsorption mechanism. This method is expected to be applicable for not only the nuclear power researches, but also studies on nanotechnologies.
 coated by 2D materials
coated by 2D materialsOgawa, Shuichi*; Yusa, Ryunosuke*; Wang, G.*; Pettes, M. T.*; Liu, F.*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Abukawa, Tadashi*; Moody, N. A.*; Yamaguchi, Hisato*
no journal, ,
Lanthanum hexaboride (LaB ) has a low work-function and is widely used as a thermionic cathode. For practical application, further reduction of its work-function and high durability have been required. In this study, the effect of 2D material coating materials (graphene and hexagonal boron nitride (hBN)) prepared by a wet-transfer method on the work-function of LaB
) has a low work-function and is widely used as a thermionic cathode. For practical application, further reduction of its work-function and high durability have been required. In this study, the effect of 2D material coating materials (graphene and hexagonal boron nitride (hBN)) prepared by a wet-transfer method on the work-function of LaB (100) was studied by using photoelectron emission microscopy (PEEM), synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy and DFT calculations. PEEM images for samples after 905
(100) was studied by using photoelectron emission microscopy (PEEM), synchrotron radiation photoemission spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy and DFT calculations. PEEM images for samples after 905 C heating clearly showed strong photoemission in the hBN coating region. DFT calculations indicated that the work-function increases in graphene due to the inward dipole formation, while the work function decreases in hBN due to the outward dipole forming at the interface.
C heating clearly showed strong photoemission in the hBN coating region. DFT calculations indicated that the work-function increases in graphene due to the inward dipole formation, while the work function decreases in hBN due to the outward dipole forming at the interface.

Ogawa, Shuichi*; Yusa, Ryunosuke*; Wang, G.*; Pettes, M. T.*; Liu, F.*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Abukawa, Tadashi*; Moody, N. A.*; Yamaguchi, Hisato*
no journal, ,
LaB has been used as a thermionic cathode due to its low work function, but it is also expected to be used as a photocathode by further lowering the work function. Here, we report photoemission electron microcopy (PEEM), thermionic emission electron microscopy (TEEM) and synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (SR-XPS) study on the work function change of LaB
has been used as a thermionic cathode due to its low work function, but it is also expected to be used as a photocathode by further lowering the work function. Here, we report photoemission electron microcopy (PEEM), thermionic emission electron microscopy (TEEM) and synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (SR-XPS) study on the work function change of LaB by coating with two-dimensional materials (graphene and hexagonal boron nitride (hBN)). A larger decrease of work function for the hBN coated LaB
by coating with two-dimensional materials (graphene and hexagonal boron nitride (hBN)). A larger decrease of work function for the hBN coated LaB (100) compared to graphene coated LaB
(100) compared to graphene coated LaB (100) was observed and qualitatively explained by our density functional theory (DFT) calculations.
(100) was observed and qualitatively explained by our density functional theory (DFT) calculations.